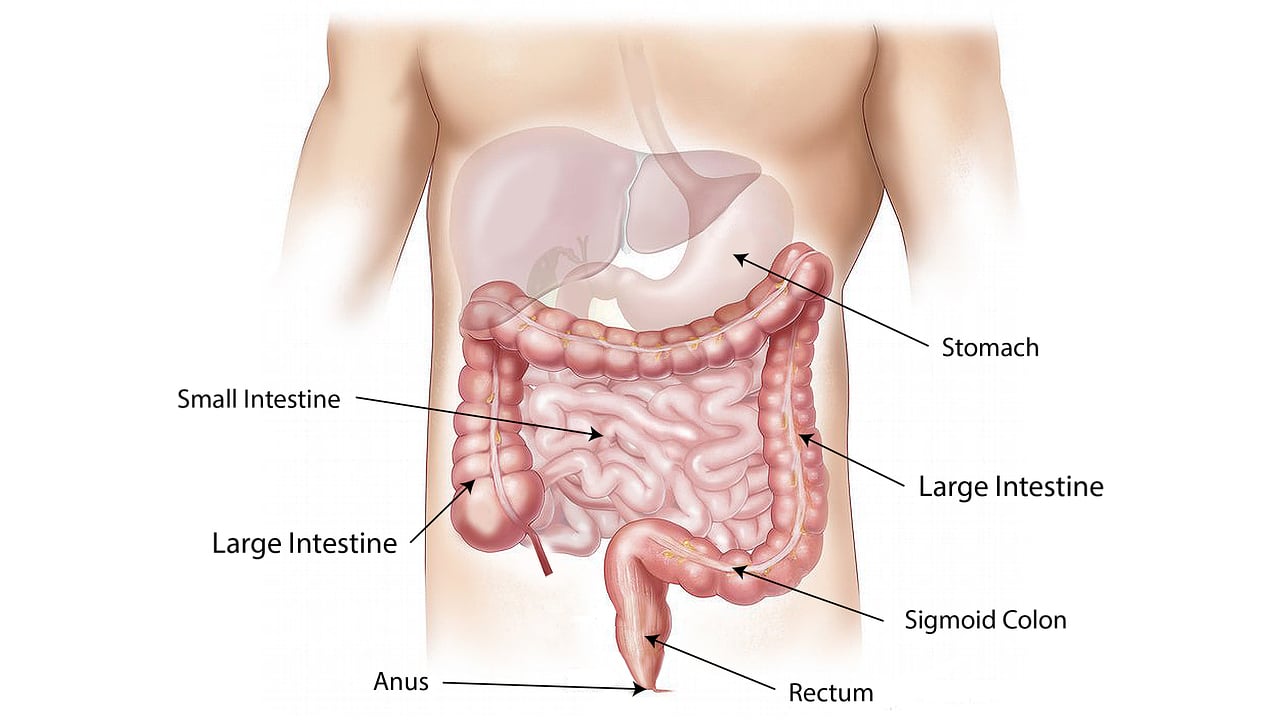
Crohn’s disease is a chronic illness that affects the digestive system. It causes inflammation and irritation particularly affecting the small intestine, which is connected to the large intestine and the colon, altough it can also affect the whole gastrointestinal tract.
This disease leads to intestinal ulcers, which can cause fistulas or narrowings of the intestinal tract, symptoms that must be treated surgically. However, the disease can also occur after any interventions.
Causes
Not all Crohn’s disease’s causes have yet been discovered through studies. It’s commonly believed that this inflammation can be triggered by a combination of multiple causes.
Studies have shown a family correlation, like a parent or a sibling who already contracted the disease spreading it to other family members. However, this theory is still a topic of research and debates.
The disease can occur from an autoimmune reaction. For instance, from an immune system’s “attack” to healthy cells, caused by some bacteria in the intestinal system.
Smoking or taking anti-inflammatory, antibiotic or contraceptive drugs can also trigger Crohn’s disease. All these things, complete with an unhealty diet, seem to increase the chances of contracting the disease.
Symptoms
There are various symptoms related to this disease:
– Diarrhea
– Traces of blood in the feces
– Abdominal pain
– Flatulence and bloating
– Weight loss without no apparent reason
Since all these symptoms can also relate to other diseases, Crohn’s disease gets often diagnosed late or even almost by accident, through specific examinations.
The diagnosis
There are a lot of clinical exams to diagnose Crohn’s disease. In NefroCenter’s diagnostic centers, it’s possible to get reservations for specific medical examinations to diagnose and keep intestinal inflammations under control.
Colonscopy with intestinal biopsies, useful for spotting any inflammatory-related changes in the intestinal tissues. That’s an examination that needs to be periodically repeated to keep the disease under control.
Digital chromoendoscopy can complement the regular colonscopy to help obtaining a more detailed image of the tissues.
There are also other equally invasive methods. The esophagogastroduodenoscopy is useful for identifying any presence of the disease in the upper part of the intestine.
Enteroscopy with the use of the video capsule is used to identify any lesions to the small intestine, therefore in areas not accessible by regular colonscopy.
An additional examination can be done through surgical exploration, with the patient subjected to anesthesia. This practice is particularly used for the peranial Crohn’s disease.
There are also many other less invasive examinations to keep the intestinal walls under control. One of them is the abdominal ultrasound, that allows to check and examine the various areas of the apparatus.
The abdominal magnetic resonance with contrast agent is also non-invasive, and thanks to it it’s possible to check any inflammed area. The contrast agent can either be injected or taken orally.
Therapies to Crohn’s disease
Crohn’s disease’s cures are focused on fighting the intestinal inflammation through various treatments. If there are any complications, the therapy can involve the use of intestinal antibiotics.
A significant action against inflammation is guaranteed by steroids, cortisone-based medicines that act efficiently through the whole body.
Other drugs that can be used in this kind of therapies are azathioprine, 6-mercaptpurine or metrotrexate, all belonging to the immunosuppressants category, which inhibit white blood cells’ functions responsible for inflammation.
Additionally, biological drugs can also be taken. They’re useful to spread monoclonal antibodies to block the molecules responsible for the inflammation.
Medical research has also opened the gates to therapies for Chrohn’s disease involving mesenchymal stem cells, particularly used for a more effective treatment of complex perianal fistulas compared to other therapies.
If any irreversible complications occur, with the use of drugs proving ineffective, the only way left would be surgical therapy.
An healthy diet to fight Crohn’s disease
Dietary regimes can vary according to the different stages of the disease. In the chronic stage (therefore not acute), the diet isn’t too much restrictive. First of all, the patient must avoid drinking milk or eating dairy products and food that contains significant amounts of lactose in general.
Sugar and salt, alcoholic drinks, stinging spices (like chilli, pepper, ginger, and so on) also have to be avoided, the mushrooms as well.
In the chronic stage, cooking methods are just as equally important. Some of them are recommended for those affected by the disease. Boiling, steaming sous-vide cooking, pressure cooking and low temperature cooking are all recommended.
On the other hand, fried and grilled food can be extremely harmful.
Braising, stewing, sautéing and oven roasting food must be eaten in moderation to avoid ingesting too much fat.
This diet should never lack carbohydrates and soluble fibers, useful for the nourishment and the correct functioning of the intestinal bacterial flora.
Diet in the acute stage
During the acute stage, the diet must be low in fibers, therefore low in whole grains, vegetables, legumes and fruit, with the exception of potatoes and bananas.
Patients that go through a severe stage of the disease must opt for a total enteral nutrition. That consists of introducing the food through a nasogastric tube or by mouth.
This kind of nutrition is particularly indicated for malnourished patients and can be integrated with drug therapy.